Normal Blood Glucose Levels: Key Symptoms and Why Testing Matters

Do you know what blood sugar is? It’s the concentration of glucose in our blood, and it plays a crucial role in our overall health. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is key to preventing or managing diabetes. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the standard range for normal blood sugar levels, and how to effectively manage them.
〈More Info:How to Use a Glucose Meter and Test Strips: Easily Manage Your Blood Sugar at Home!〉
What are normal blood sugar levels? Both high and low levels can be problematic.
The concentration of glucose in our blood is crucial to our health. The normal range for fasting blood sugar is 70-99 mg/dL, and blood sugar levels two hours after a meal should be below 140 mg/dL. Those familiar with blood sugar may also know about HbA1c, which measures the average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months; the normal range for HbA1c is below 5.7%. These metrics help assess whether our blood sugar levels are well-controlled, which is vital for preventing diabetes and its complications.
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is typically caused by insufficient insulin production or ineffective insulin action. Common symptoms include frequent urination, thirst, fatigue, and blurred vision. Prolonged high blood sugar levels increase the risk of diabetes and can lead to serious complications like cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve injury. Persistent hyperglycemia can significantly impact quality of life, making stable blood sugar control crucial for maintaining overall health.
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, occurs when blood glucose levels fall below the normal range. It is often caused by excessive insulin, irregular meals, or intense physical activity. Symptoms can include dizziness, palpitations, sweating, and trembling. In severe cases, loss of consciousness may occur. Chronic hypoglycemia can impair brain function and affect daily life and overall health. To prevent low blood sugar, it's recommended to regularly monitor blood glucose levels and maintain a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
Blood Glucose Normal Range
| Index | Normal | Pre-diabetes | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting Blood Sugar | 70-99 mg/dL |
100-125 mg/dL |
≥126 mg/dL |
|
Postprandial Blood Sugar |
<140 mg/dL |
140-199 mg/dL |
≥200 mg/dL |
|
HbA1c |
<5.7% |
5.7%-6.4% |
≥6.5% |
Blood Glucose Levels for Diabetes
The diagnosis of diabetes primarily relies on fasting blood glucose, postprandial blood glucose, and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels. According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), normal blood sugar ranges are as follows: fasting blood glucose should be below ≥126 mg/dL, postprandial blood glucose (measured two hours after eating) should be below ≥200 mg/dL, and HbA1c should be below ≥6.5%. However, these benchmarks can vary depending on the individual patient’s condition. We will detail these indicators further below.
〈Products:In Vitro Diagnostics-Diabetes Care〉
Blood Glucose Control Ranges for Type 1 Diabetes in Children
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that typically develops in children or adolescents. This disease causes the immune system to attack and destroy the βcells in the pancreas, leading to insufficient insulin production and elevated blood glucose levels. Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, and weight loss. For children and adolescents with Type 1 diabetes, it is recommended to maintain blood glucose levels within the following ranges: fasting blood glucose between 80-130 mg/dL, and blood glucose two hours after meals below 180 mg/dL, to minimize the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Blood Sugar Control Range for Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes in adolescents is similar to that in children; it is an autoimmune condition typically diagnosed during adolescence. This disease results from the immune system attacking the β cells in the pancreas, leading to insufficient insulin production. The blood sugar control targets for adolescents with Type 1 diabetes are similar to those for children: fasting blood glucose should be maintained between 80-130 mg/dL, and blood glucose levels two hours after meals should be less than <180 mg/dL. Ongoing monitoring and management of blood glucose levels are crucial for adolescents to ensure healthy growth and reduce the risk of complications.
Blood Glucose Control Range for Adults with Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes in adults is a metabolic disorder that typically develops later in life. It is characterized by either insufficient insulin production or poor response to insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. Risk factors for adult diabetes include obesity, lack of physical activity, genetics, and unhealthy eating habits. Common symptoms include frequent urination, thirst, fatigue, and blurred vision.
For adults with diabetes, the recommended blood glucose control range is typically 80-130 mg/dL for fasting blood glucose and less than <180 mg/dL for blood glucose two hours after meals. Effective management can include gradual lifestyle changes (such as dietary adjustments and increased physical activity), oral hypoglycemic medications, and insulin therapy, all aimed at controlling blood glucose levels and reducing the risk of complications.
Blood glucose control range for elderly diabetes patients
Elderly diabetes typically refers to Type 2 diabetes occurring in older adults. As people age, insulin secretion and effectiveness may decline, coupled with reduced physical activity and poor dietary habits often seen in the elderly, these factors collectively contribute to elevated blood glucose levels.
For elderly diabetes patients, the blood glucose control targets are usually more relaxed. It is generally recommended to maintain fasting blood glucose levels between 90-150 mg/dL and to keep postprandial blood glucose levels below 200 mg/dL two hours after meals.
How to Control Blood Sugar? Five Effective Methods
Maintaining blood sugar within a normal range is crucial for overall health. In the following section, we'll explore five effective strategies to help you manage your blood sugar levels easily. These tips will empower you to keep your blood sugar stable and within the normal range.
1.Dietary Control
Dietary control is always the most effective strategy! When eating, opt for low-GI foods like whole grains and green vegetables. Aim to eat smaller, more frequent meals and avoid consuming too many sugary drinks and high-sugar foods. These practices can effectively stabilize blood sugar levels.
2.Regular Exercise
Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise daily, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can help improve insulin sensitivity and promote blood sugar metabolism.
3.Medication Therapy
If maintaining stable blood sugar levels through diet and exercise proves challenging, it's essential to seek medical advice. Taking prescribed diabetes medications or insulin on time can help prevent blood sugar from becoming too high or too low.
4.Regular Monitoring
For diabetes patients, regularly monitoring and recording daily blood sugar levels is crucial. Keeping a consistent log of blood glucose readings allows doctors to adjust treatment plans promptly, ensuring that blood sugar remains within the normal range.
5.Stress Management
Stress can sometimes impact blood sugar levels. Learning relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can help stabilize blood glucose levels and reduce the impact of emotional fluctuations on your blood sugar.
How Often Should You Check Your Blood Sugar? Regular Monitoring Is Essential!
Regular blood sugar monitoring is a crucial step in maintaining your health. By detecting any abnormalities in your blood sugar levels early, you can promptly adjust your diet and treatment plan, preventing potential health issues from worsening.
Benefits of Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
1.Early Detection of Abnormalities
Regular blood sugar checks allow for the timely identification of any irregularities, enabling quick adjustments to your diet and treatment plan. This proactive approach helps prevent potential issues from escalating.
2.Preventing Complications
Maintaining proper blood sugar levels reduces the risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease and kidney problems. Keeping your blood sugar within a healthy range is crucial for overall well-being.
3.Personalized Treatment
Routine monitoring provides data that can be used to tailor medication and lifestyle adjustments according to your specific needs, enhancing the effectiveness of your treatment and making health management more targeted.
Recommended Blood Sugar Testing Frequency
● Normal Individuals: Test once a year.
● Pre-diabetic Individuals: Test every six months.
● Diabetic Patients: Test 1-4 times daily, depending on the condition and doctor's advice.
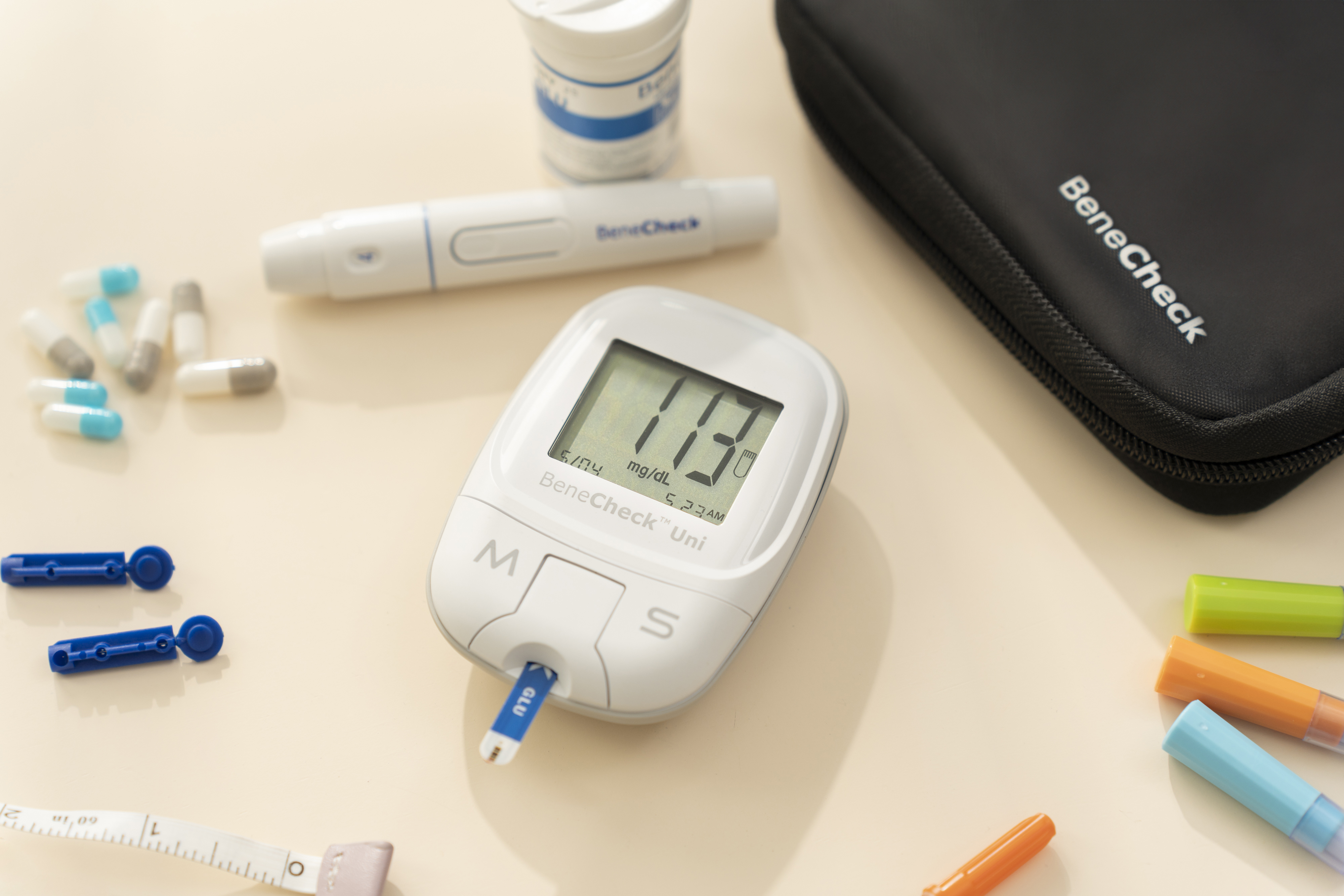
BeneCheck Uni Blood Glucose Monitoring System
When selecting a blood glucose monitor, it's essential to consider key factors such as measurement accuracy, ease of use, and support from a reputable brand with reliable after-sales service. This ensures that assistance is available if repairs are needed. BeneCheck Uni Blood Glucose Monitoring System is a professional and precise device that uses glucose dehydrogenase technology to minimize interference from varying blood oxygen levels, guaranteeing accurate readings. This monitor is not only compact and portable but also certified by both TFDA and CE, making it a trustworthy choice. Additionally, it offers an optional Bluetooth feature for added convenience, fully meeting your health management needs
〈Recommendation:BeneCheck Uni Blood Glucose Monitoring System〉
Conclusion
If you are in search of a reliable and high-quality blood glucose monitor, General Life Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (GLB) from Taiwan stands out as your top choice. GLB's blood glucose monitors, with our advanced technology and precise measurement capabilities, make it easy to effectively manage your blood sugar levels. Whether you are a diabetic patient or simply need to monitor your blood glucose, GLB's devices provide accurate and prompt data. For more information about the Benecheck blood glucose monitors, feel free to contact us.
Reference
〈Reference:奇美醫院糖尿病衛教〉
〈Reference:美國糖尿病協會(ADA)〉

